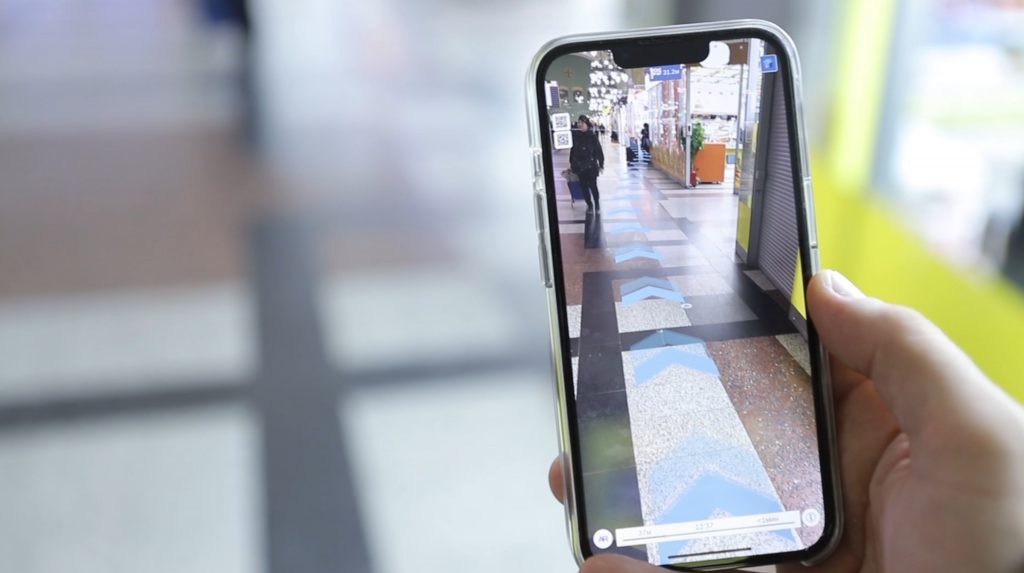
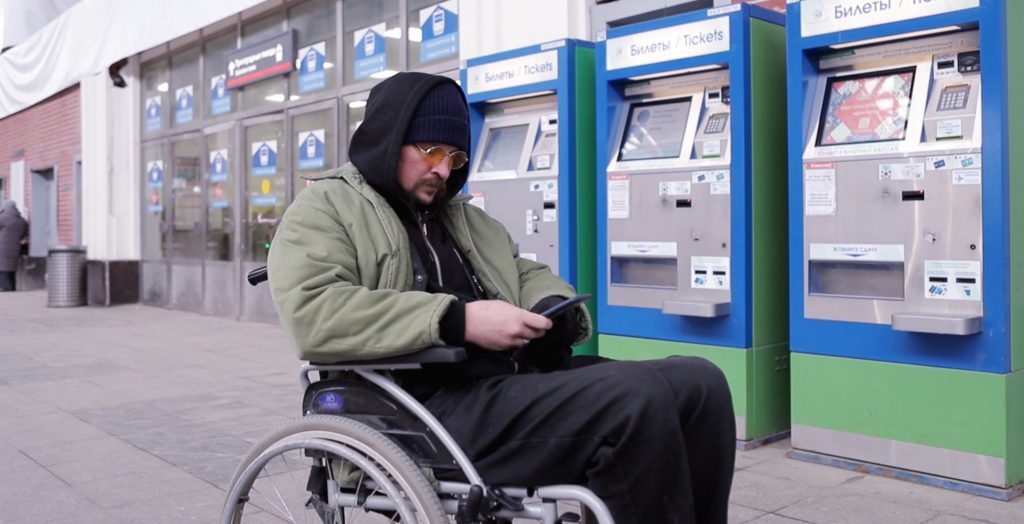
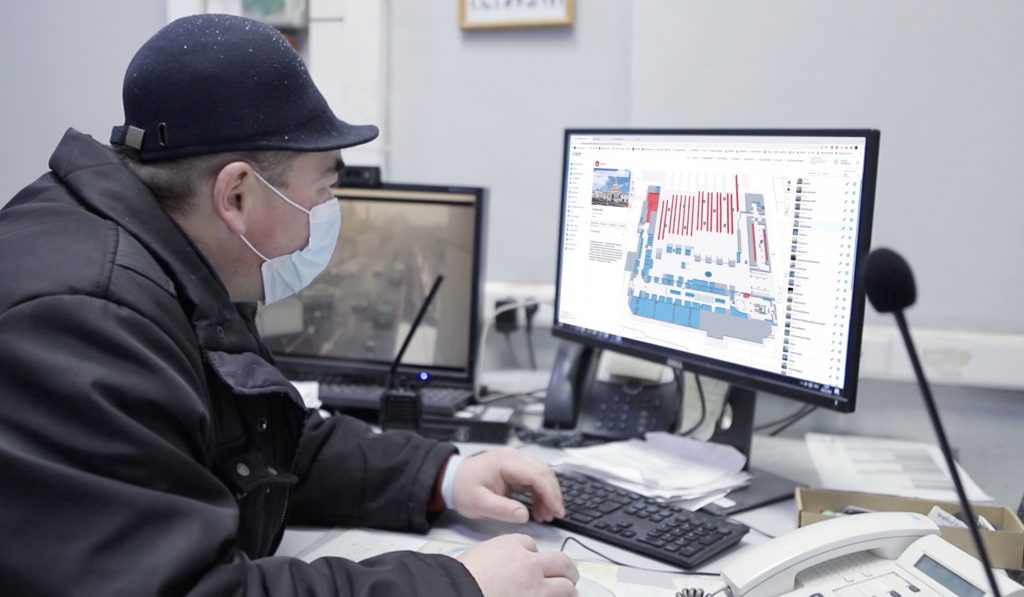
Пандемия значительно увеличила нагрузку на работников здравоохранения из-за высокого числа пациентов в критическом состоянии, сокращения препаратов и повышения рисков заболевания. Для многих сотрудников возросшая нагрузка и нехватка персонала привели к увеличению продолжительности рабочего дня. Руководство в здравоохранении всегда ищет новые способы удержания и привлечения персонала, необходимо пересмотреть текущие действия и предоставить сотрудникам необходимую поддержку. Технологии интернета вещей и системы определения местоположения в реальном времени (RTLS) внутри помещений способны предоставить решения для более эффективного распределения нагрузок на ваш персонал.
Американская ассоциация медсестер интенсивной терапии опросила более 6000 сотрудников и обнаружила, что 66% считают, что высокие нагрузки во время пандемии заставили их задуматься о смене работы. При этом каждый пятый медработник уже вообще ушел из медицины.
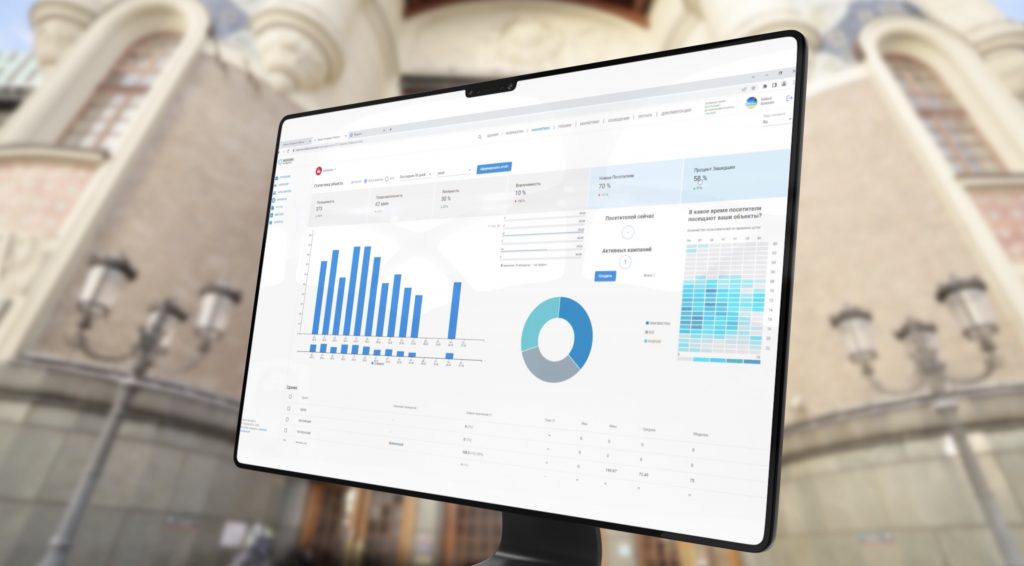
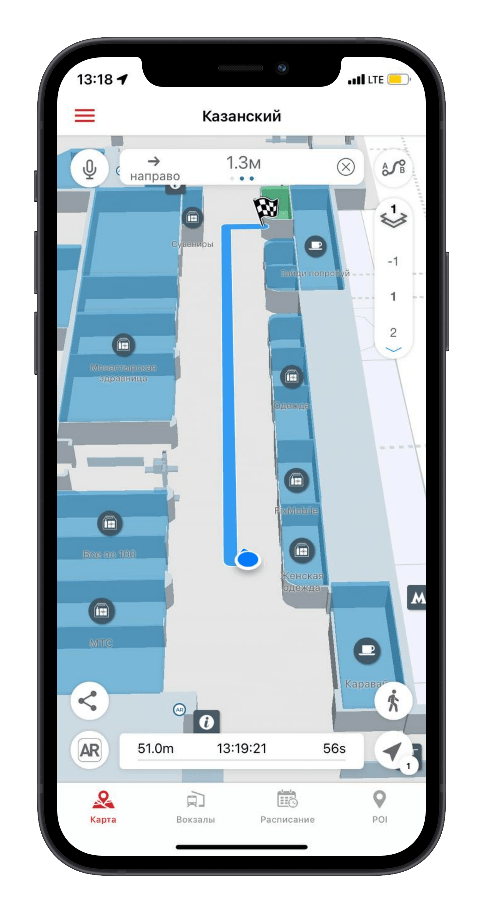
Платформа INP используют различные технологии навигации, метки, бейджи и датчики с поддержкой IoT для отображения в помещении местоположения медицинского оборудования, персонала и пациентов. Использование такой системы сокращает время, затрачиваемое персоналом на поиск и получение критически важных активов, автоматизирует процессы и предоставляет руководству актуальную аналитику, позволяющую понять сложные места рабочего процесса в поликлинике или больнице. Возможности цифровизации процессов поликлиники, в том числе навигация в ее помещениях, управления активами и рабочими процессами, облегчают нагрузку на персонал и позволяют им сосредоточиться на самом важном — уходе за больными.
Системы определения местоположения в реальном времени: вложение в медицинский персонал
Руководство больниц знает, что мед персонал играет главную роль для успешного лечения пациентов. Это особенно актуально для больниц, в которых высокая текучка кадров. Сохранение квалифицированных и опытных медсестер является первоочередной задачей.
Новые технологии цифровизации больницы и навигации внутри ее помещений могут помочь сделать работу в сфере здравоохранения более приятной, безопасной и эффективной. Давайте рассмотрим четыре основных направления применения наивигации внутри поликлиники и больницы.
Управление активами
Каждая третья медсестрав среднем в течение смены они тратят более часа на поиск нужного оборудования. Это почти 60 часов в месяц, которые тратятся впустую вместо ухода за пациентами. Внедрение навигационной платформы для помещений в больнице позволит медицинскому персоналу найти критически важное оборудование с помощью меток в течение нескольких минут, что экономит драгоценное время, снизит нагрузку и обеспечивает своевременное оказание помощи пациентам.
Наша платформа предоставляет карты помещений и территорий в режиме реального времени, список медицинского оборудования с расположением на карте, отчеты об использовании того или иного оборудования, иформирование о его техническом обслуживании. Автоматизируя управление запасами (PAR) учреждения могут обеспечить постоянную доступность медицинских устройств. Программные решения INP представляет собой панель управления и удобное мобильное приложение, чтобы предоставить лицам, осуществляющим уход, информацию о состоянии оборудования или запросов на складе. Администраторы могут использовать серверную часть системы INP для мониторинга уровней PAR и выявления неэффективных рабочих процессов или пополнения запасов.
Автоматический вызов медсестры
Чтобы внедрить автоматизированную систему вызова, больница может легко интегрировать INP с имеющейся системой вызова медсестер, создавая относительно простое решение с большими преимуществами.
Когда лицо, осуществляющее уход, входит в палату пациента, его бейдж со встроенной меткой автоматически отправляет сигнал, который отменяет вызов и точно фиксирует время прибытия к больному и время ухода от него. Это решение позволяет немедленно сосредоточиться на потребностях пациента, экономит время и повышает качество обслуживания. Кроме того, автономные данные помогают контролировать персонал в связи с ответственностью или обвинениями в качества обслуживания пациентов. Аналитические данные, предоставляемые системой INP, помогают улучшить работу внутренних процессов учреждения и распределить ресурсы в часы максимальной нагрузки.

Клинические рабочие процессы
В дополнение к внедрению автоматизированной системы вызова медсестер медицинские учреждения могут использовать INP для устранения узких мест в рабочем процессе поликлиники и улучшения общей координации ухода за пациентами. Используя аналитический модуль системы INP, медицинские работники могут следить за ключевыми показателями потока пациентов, такими как их количество, продолжительность пребывания, используемые палаты, время ожидания пациента и время, проведенное с врачом.
Персонал может находить узкие места при взаимодействии пациентами, маршруты передвижения по больнице, а также о усредненных по дням и часам данные от отдельных пациентов. Руководство больницы может использовать эту информацию и оптимизировать работу в требуемых областях. После установки Indoors Navigation Platform в медицинских учреждениях сократится время простоя пациентов, что приведет к повышению их лояльности.
Система оповещения персонала и меры безопасности
Насилие в медицинских учреждениях обострилось во время пандемии. С начала пандемии COVID-19 резко возросло насилие в отношении медицинских работников, а в некоторых больницах число опасных инцидентов увеличилось более чем на 50 процентов. Решение по безопасности от Индорс Навигейшн с поддержкой IoT создает надежную систему оповещения в режиме реального времени с привязкой к положению в здании больницы, которая предотвращает перерастание угроз в насильственные ситуации, предоставляя медицинским работникам возможность незаметно отправлять оповещения группе безопасности с помощью кнопки быстрого доступа на бейдже.
После нажатия бейдж немедленно сообщает о местонахождении сотрудника на карте диспетчеру службы безопасности. Решение также интегрируется с традиционными системами безопасности, сервисами управления видео, контроля доступа, а также различными сторонними приложениями с API.
Выбор лучшего решения для вашей больницы
При выборе навигационного решения нахождение стратегического партнера с комплексным набором решений упрощает расширение системы с течением времени для других аспектов эксплуатации предприятия. Во многих медицинских учреждениях, увидев информацию, обеспечиваемую RTLS, и ощутимую отдачу от первоначальных инвестиций, медицинские бригады и руководство поощряются к дальнейшему развитию своих RTLS. Ранние инвестиции в правильного стратегического партнера позволяют руководству улучшить существующую системную инфраструктуру, чтобы лучше поддерживать медицинских работников и пациентов.
Последние два года спрос на услуги здравоохранения ростет в геометрической прогрессии и нет никаких признаков его замедления. Навигационные решения для помещений, работающие на устройствах с поддержкой IoT, является важным ресурсом для здравоохранения, безопасности и эффективности медицинских работников. В здравоохранении нужны решения по автоматизации рабочих процессов, которые помогут персоналу работать эффективнее. Этот подход улучшает результаты и безопасность пациентов, одновременно снижая операционные затраты на оказание помощи.