When we hear about 5G, the first thing that comes to mind is the incredible download speed and ultra—high-quality video streaming. However, behind this facade of "speed" lies a much more revolutionary opportunity: accurate positioning of objects in real time indoors. 5G technology is transforming from a tool for content consumption into an infrastructure framework for the digital twin of the physical world. In this article, we will explain exactly how fifth-generation networks open up a new era for navigation inside buildings.
Why is 5G a breakthrough for Indoor Positioning?
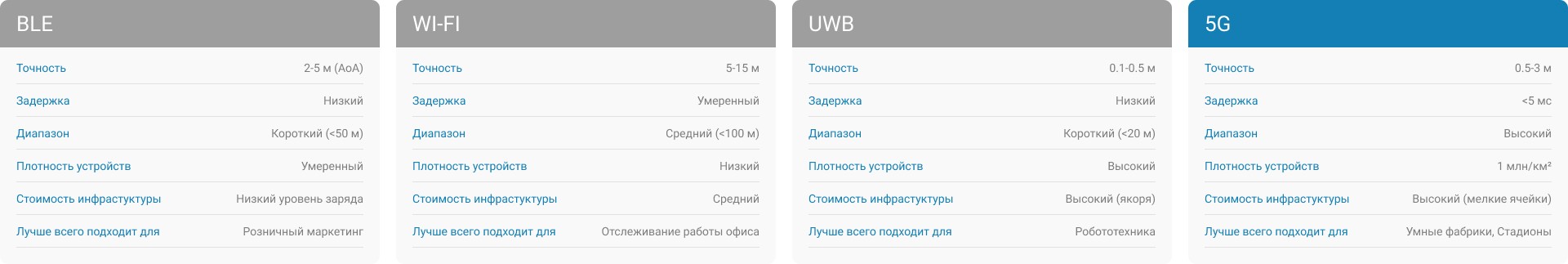
Traditional methods like Wi-Fi or Bluetooth (BLE) are good at rough positioning, but face limitations in accuracy, stability, and scalability. 5G approaches the task with a different, systematic approach, using its fundamental advantages:
This year, 5G technology has finally moved from the consumer service stage to the category of critical industrial infrastructure. Thanks to the adoption of 3GPP Release 16 and 17 standards, this technology has acquired its own built-in function of high-precision positioning inside buildings, creating direct competition with established solutions, for example, based on Wi-Fi RTT.
Of particular importance is Release 17, which transforms 5G from a tool for commercial use into a solution for industry. The centimeter accuracy implemented in it allows 5G to compete on equal terms not only with Wi-Fi RTT, but also with UWB solutions in the most important areas, such as occupational safety and control of hazardous areas. As a result, enterprises are able to use a single network for both communication and data exchange, as well as for accurate tracking, consolidating infrastructure.
5G-based positioning solutions differ in a different, systematic approach, using their fundamental advantages:
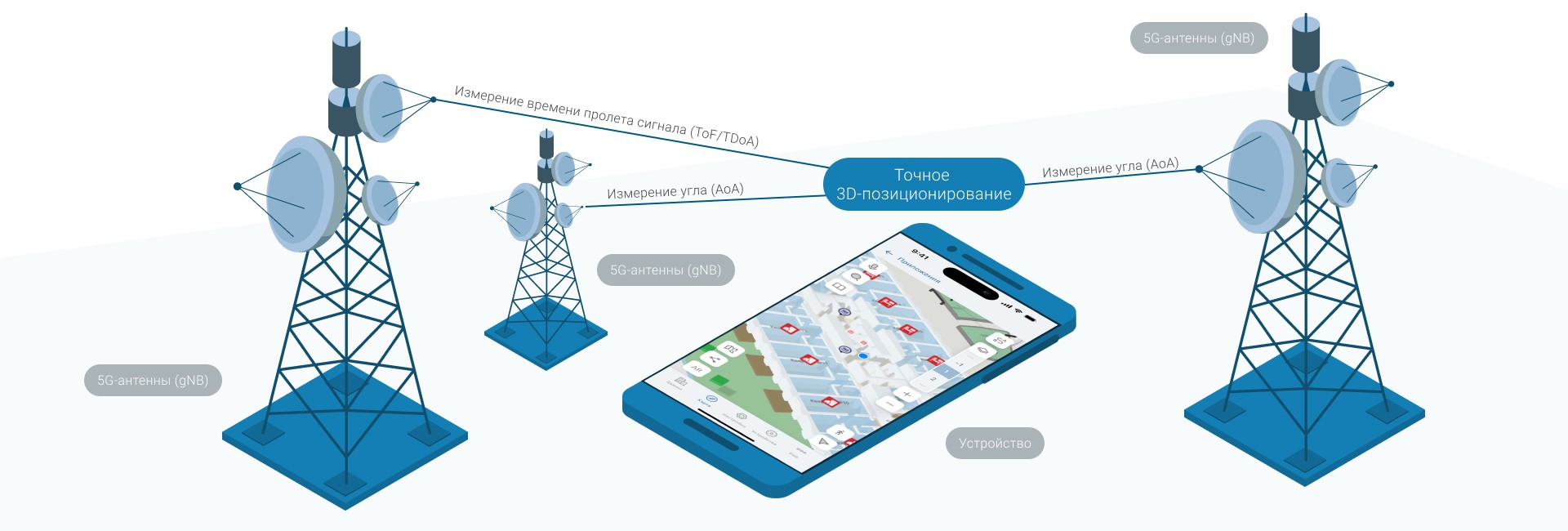
Swiss Handouts (Ultra-reliable Low-latency Communication - uRLLC): Data exchange between the device and the base station is almost instantaneous. This is critically important for applications where every millisecond is important: controlling autonomous equipment or medical devices.
MIMO (Multiple input and Multiple output): The antennas of 5G stations can simultaneously form dozens of narrowly focused beams, communicating with a variety of devices. This allows you not only to establish the fact of the connection, but also to accurately determine the angle of arrival of the signal (Angle of Arrival - AoA), which is the key parameter for calculating the position.
High frequencies (millimeter waves): Although they have a shorter range, their use allows for unprecedented measurement accuracy. signal flight time (Time of Flight - ToF). The combination of distance (ToF) and direction (AoA) data gives accurate 3D coordinates.
How does this work in practice? Key positioning methods in 5G
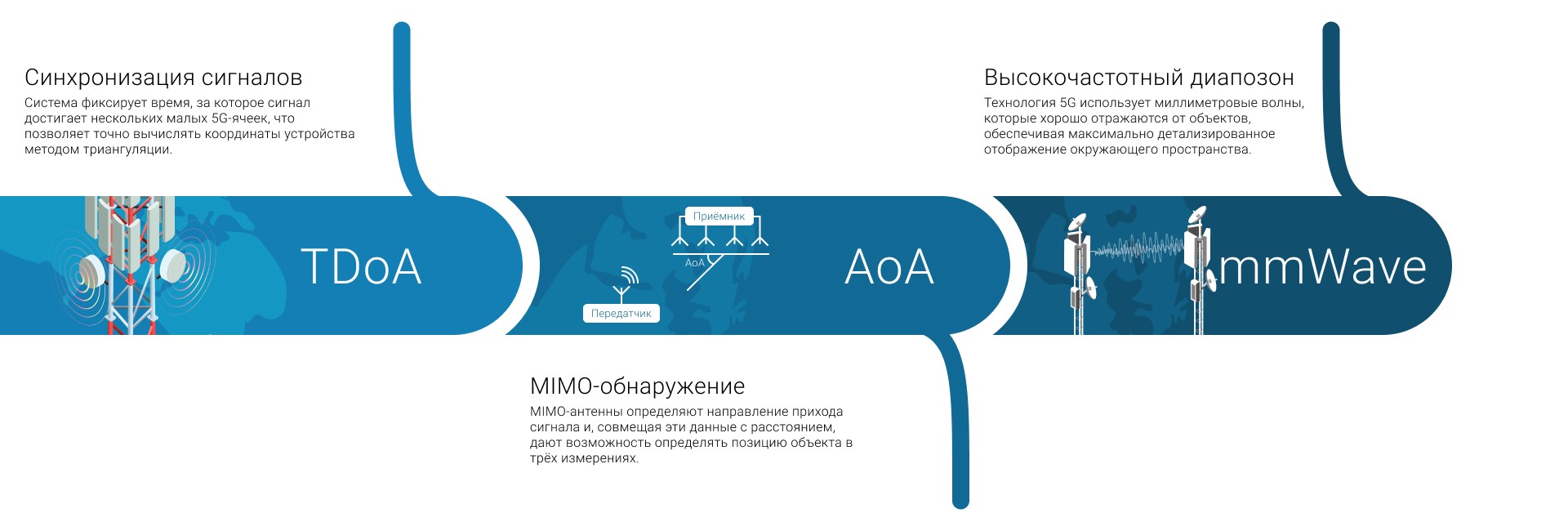
5G standards are initially tailored for navigation. Unlike previous generations, where positioning was a byproduct, in 5G it is one of the basic functions. The main methods used in fifth generation networks include:
Long-term broadcast using TDoA (Arrival time difference): The device sends a signal that is received by several base stations. Since the signal reaches them at slightly different times, the system calculates the difference with the highest accuracy and, knowing the location of the stations, determines the location of the device. According to research (for example, in the materials arxiv.org ), this method can provide an accuracy of up to 1 meter under ideal conditions.
Positioning by angle of arrival and angle of deviation (AoA/AoD - Angle of arrival/departure): Massive MIMO 5G antennas are able to detect at what angle the signal came from the device or at what angle it needs to be sent. By combining data on angles from several stations, the system "draws" the location of the object with geometric accuracy.
Millimeter Wave Technology (mmWave): A key feature of 5G is the use of millimeter waves (mmWave) in the high-frequency spectrum (from 24 GHz). Their physical property — short length — leads to the fact that the signal is repeatedly reflected from objects, forming a dense network of signal beams. Special AI algorithms process this complex pattern of reflections, which eventually makes it possible to scan and map the interior with exceptional accuracy.
In practice, these methods are often combined to eliminate interference and increase reliability.
Areas of application: from smart factories to hyper-personalized retail
Accurate indoor positioning using 5G is not a theoretical task, but a technology that is already changing business processes.
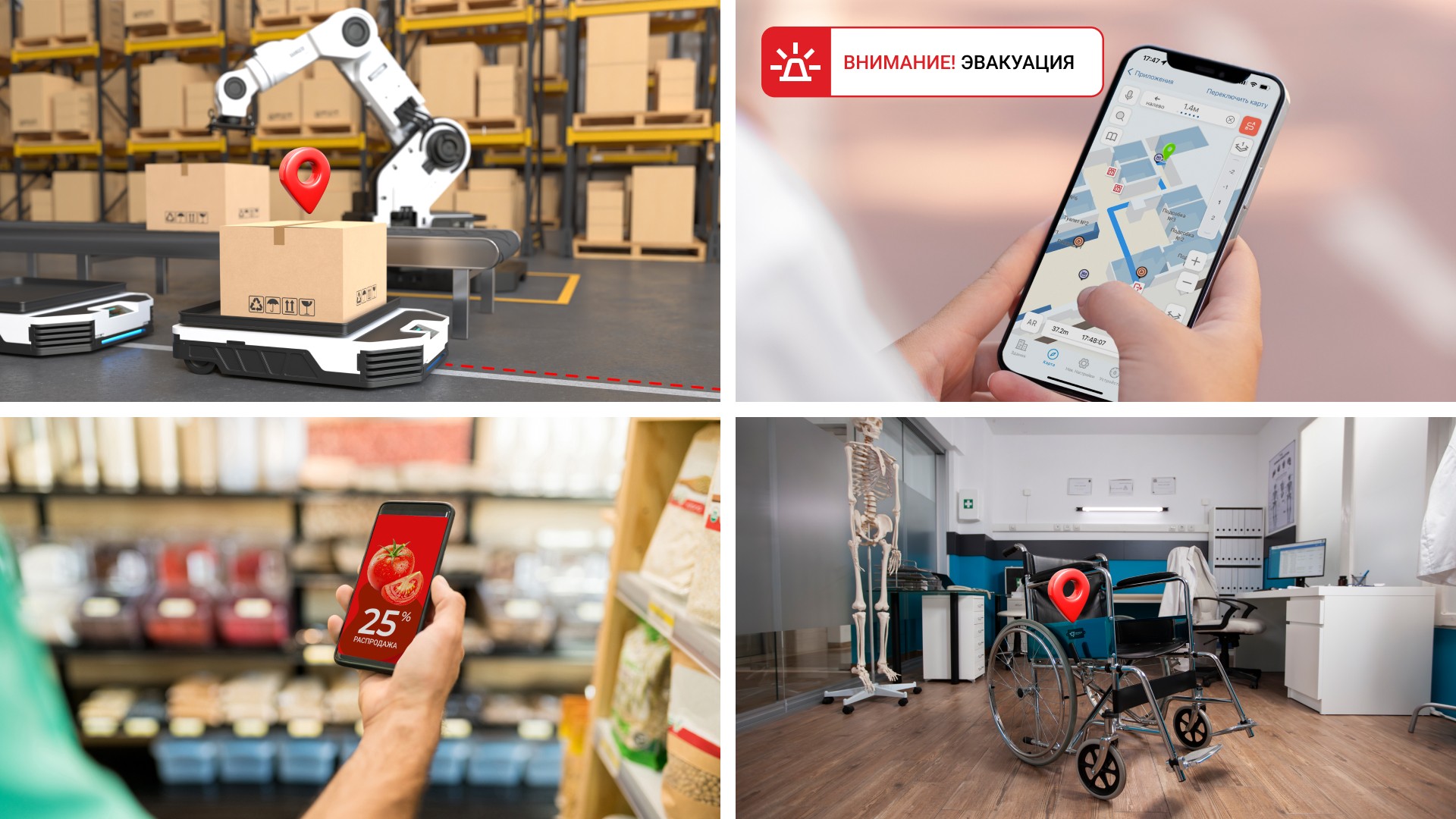
Smart Factories and Logistics (Industry 4.0): Imagine a warehouse where autonomous loaders and robot pickers move along perfectly aligned routes without collisions. 5G allows real-time tracking of not only machinery, but also every product, tool, or container, optimizing supply chains and minimizing downtime.
Safety and emergency management: In the event of a fire or smoke in a large shopping mall or office, the system can accurately locate each person on their smartphone and plot a personalized evacuation route for them on the mobile application display. Rescuers will know exactly where the victims are.
Retail and personalized marketing: The mall can offer customers navigation to the desired store. But more importantly, visitor flow analytics are becoming incredibly accurate. Where do people stay more often? Which way do they choose? This allows you to optimize the product layout and send relevant discounts and offers in real time when the customer is in close proximity to the product.
Healthcare: Tracking expensive medical equipment, monitoring the movement of patients with cognitive impairments within the hospital, organizing the work of mobile disinfection robots - wherever accuracy and reliability are important, 5G finds its application.

The future and challenges
Despite the potential, the massive adoption of 5G positioning is facing challenges. Indoor coverage density should be high, especially for the use of millimeter waves. There are issues of standardization and the cost of infrastructure deployment. However, as noted in various scientific publications, the future belongs to hybrid solutions, where 5G will act as a high—precision "skeleton" of navigation, and technologies like BLE or motion sensors will be "muscles" providing final, ultra-precise localization at a specific point.
Finally
5G is much more than just "fast internet". 5G positioning is already becoming a reality. This is a new nervous system for smart buildings, which gives them the ability to accurately "feel" and track what is happening inside. Company Indoors Navigation it is at the forefront of these technologies, developing solutions that integrate the power of 5G to create a future where every room becomes smart, safe and efficient.
Leave a request for: https://indoorsnavi.pro/
👇 Subscribe and keep up to date with innovations! 👇







20 thoughts on “5G позиционирование в помещениях: не просто быстрый интернет, а точная навигация”
Безопасность – это главное, отлично, что над этим работают
Интересно, когда 5G станет доступен повсеместно
Проблемы с навигацией обещают решиться раз и навсегда
технология впечатляет, буду следить за новостями
навигация в помещениях станет намного проще.
Хочется видеть больше примеров из практики!
5G действительно раскрывает новые горизонты!
Это большой шаг вперед для навигации в помещениях
интересно, как повлияет на ритейл и потребительский опыт
Это просто фантастика! Надо следить за такими новинками
Не думала что технологии могут быть такими мощными)
Невероятно, 5G действительно меняет правила игры в навигации
Если 5g получит распространение, организовать позиционирование просто обязательно
интересный материал: хорошо показано, что 5G — это не про скорость, а про новую инфраструктуру точной навигации и управления внутри зданий.
Потрясающе, как стандарт Release 17 реально меняет индустрию — уже не теория, а рабочие кейсы
Вау ! Если у 5G настолько хорошая точность, что аж соперничает с UWB, то это будет очень полезно. Правда не так много телефонов сейчас поддерживают 5G и он не везде доступен
Будущее за 5G-позиционированием! С такой производительностью трудно представить каким будет будущее навигации в помещениях! Будущее доступно сегодня!
Статья получилась действительно классная — коротко, понятно и по делу.
Очень крутая и понятная разборка того, зачем вообще нужно 5G-позиционирование в помещениях
Звучит как идеальное решение для автоматизации, чтобы роботы и люди на складах работали как единый механизм без аварий и задержек.